
Prim algorithm begins by setting up a grid, where each cell is surrounded by walls. Initially, it is fully enclosed, with no passages between any of the cells, creating a solid block.
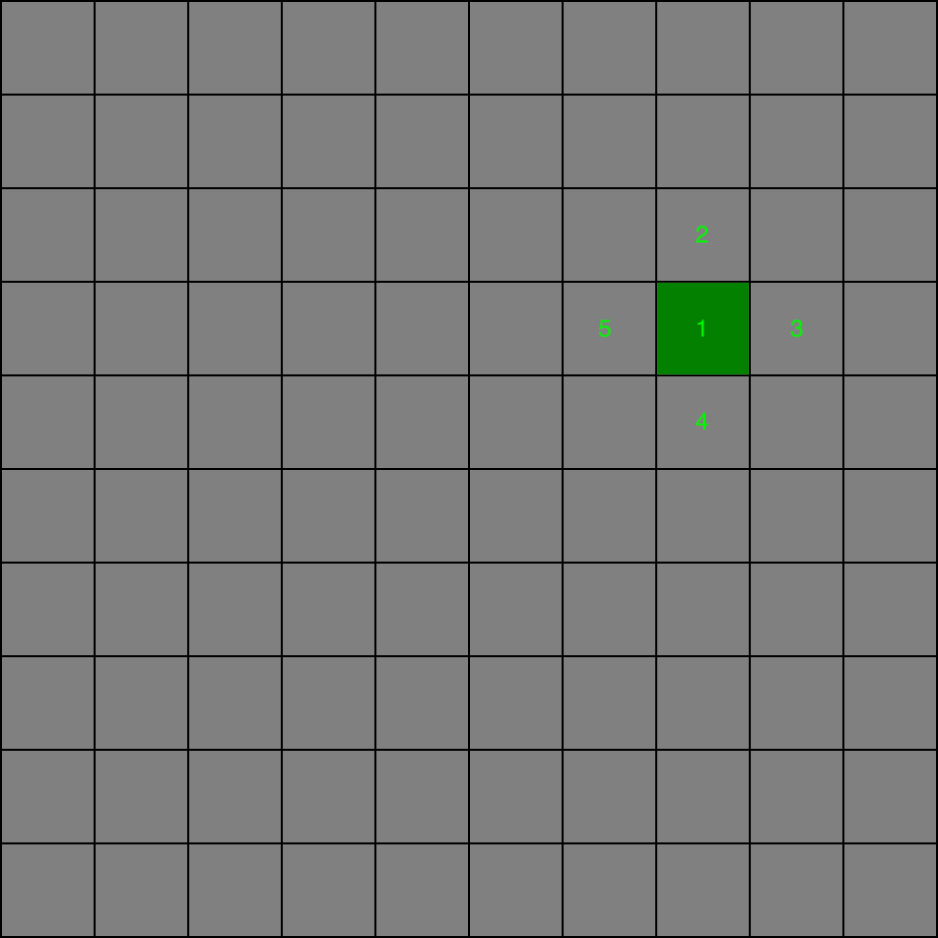
The main concept of the given algorithm is creating a dedicated list of frontier cells and running the maze generation until it gets empty. At the beginning given list is populated with one random cell. Then the cell is taken from the list with removal and marked as visited - in the given example it is cell no. 1. As a next action we fetch all of the current cells neighbours and push the non visited ones to the frontiers list, skipping the ones that are already present there. In the given case all of the neighbours will be pushed to the list - cells 2, 3, 4 and 5. None of the neighbouring cells were also visited in the current run, so the algorithm moves to the next iteration.
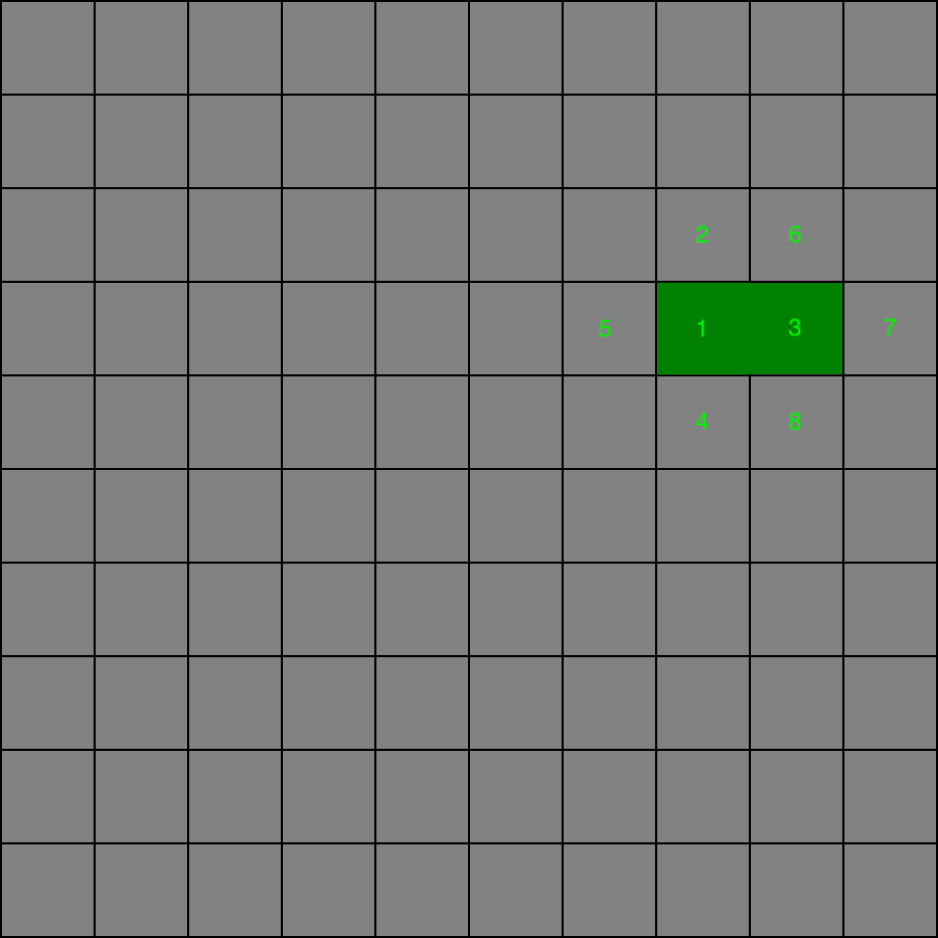
Another random cell gets selected with removal from the frontiers list and is marked as visited. In the current iteration it is the cell no. 3. As a result the cells 6, 7, 8 are pushed to the frontiers list. The cell no. 1 was already visited so instead of pushing it to the list, we remove wall between current cell and the cell no. 1. If there are more already visited cells we always pick one of them at random.
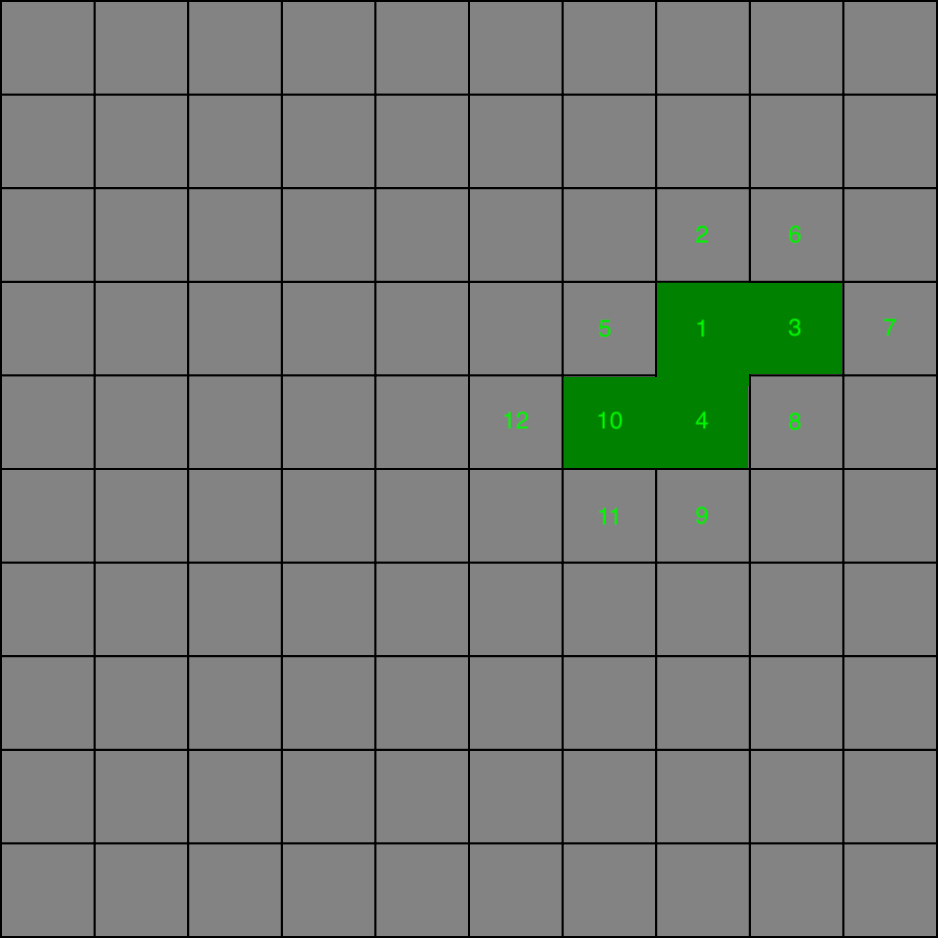
In the next iteration randomly selected frontier cell is the no. 4. The 8, 9 and 10 neighbours are pushed to the frontiers list. Cell no. 1 was already visited so it is not pushed and the wall between it and no. 4 gets removed.
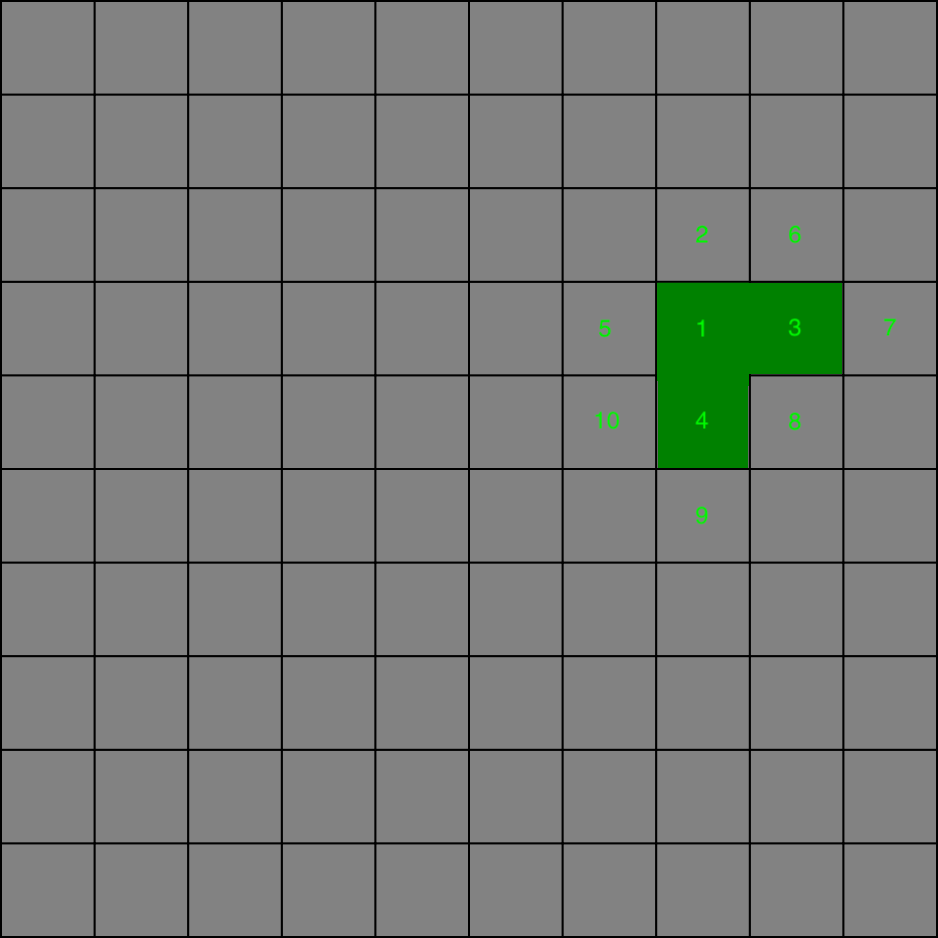

The next algorithm run randomly selects another cell. In the given case it is the no. 10. Then the no. 11 and 12 got pushed to the frontiers list. The cell no. 5 is already present there so we do not make a duplicate. Also the cell no. 4 was already visited so we do not push it. Instead we create the passage between current cell and no. 4.
Another iteration randomly selects the frontier cell no. 5. The neighbouring cells 13 and 14 got pushed to the list. Cells 1 and 10 are already visited so we do not push them to the list, instead we choose randomly the already visited cell where the passage needs to be created. As a result for the given iteration the cell no. 10 got selected so the new passage is created.

The algorithm repeats the given steps until the frontiers list gets empty. As a result all of the required passages got created and the maze is completed.
